This article is dedicated to a much missed friend,
Cheltenham novelist Sue Morgan (Zoe Barnes).

Sandford Mill
One morning I woke up and decided to do a Chelt walk – to follow the River Chelt on its entire course through the town. For sure it’s not an epic journey by anyone’s standards, but it’s still an interesting one, and big enough that I’ve had to write up the journey in two parts. This is the first.
Where to start though? To focus on the town centre, or venture out to the places it passes through on its way to Cheltenham? If so, where to draw the line? I still haven’t fully decided on that and I’m vaguely hoping to do additional walks later to extend the ground covered at either end.
The River Chelt is a modest but volatile river which rises from a cluster of springs in the hills above Cheltenham and eventually feeds into the River Severn at Wainlodes Hill. Though humble in size, it gathers momentum through its steep drop off the hills and is prone to very sudden and unpredictable flooding. It flows through Cheltenham from south-east to north-west, culverted through much of the town centre, passing through the village of Charlton Kings on its way and Arle and Uckington on the way out. The river was known as the Alr (Arle) in Saxon times, which I’ll look into in more detail in part two.

1806 map showing the course of the Chelt towards Cheltenham. (Note this map is orientated weirdly with south-west at the top.) From the bottom left corner, two separate strands of the river run side by side across the fields of Charlton Park; the mill stream, a medieval diversion, is the straighter one, while the intricately meandering stream to its left is the original natural course of the river. In the centre of the map is Sandford Mill, its millpond augmented by another small stream running down from under London Road (and which appears to originate just off Greenway Lane). Just beyond the mill, the two strands of the Chelt meet as they pass under the Old Bath Road at a site marked as Sandford Bridge – though there is no longer a bridge of any significance there today. At the top is a field called Sandford, which still survives as the upper section of Sandford Park. In the absence of any development at this time, the map singles out trees as landmarks; on the Old Bath Road there is a “Double Stemmed Tree” and roughly at the junction with what is now Thirlestaine Road, a more straggly looking specimen marked as “Seat in old Tree”. Towards the right hand side of the map is a crossroads bearing another tree, the Gallows Oak. This is the junction where the Old Bath Road and Hales Road cross London Road; marked here as “formerly Gallows Oak Turnpike”.
The river has always been a fundamental part of the town’s identity and focus and every part of it has a history. But a river walk has to start somewhere. And the first significant thing the river hits when it reaches the edge of Cheltenham is Sandford Mill.
Sandford Mill is shown (subject to obscuring trees) in the photo at the top. I couldn’t get a great picture of it because it’s a private house now and set back some way from the road and, well, I’m never quite sure about the etiquette of sticking a long zoom lens up someone’s driveway. But anyway, it’s a lovely old building with cutely rounded chimnies and has an old mill stone by the door as a relic of its former life.
I’m not entirely sure how old the present building is, but with its Cotswoldy gables it certainly looks like it’s been there since the 18th century, at which time it was worked by a well established local family of millers called Arkell. The mill site, of course, is much older. It’s possible that Sandford Mill was one of the two mills in Cheltenham listed in the Domesday Book in 1086. But even if it wasn’t, it was certainly there in the early middle ages by which time the town’s mill inventory had risen to five. It’s shown as Saundford Mill on a survey map of 1615.
Milling seems to have ceased some time in the early 1900s, and by 1911 it had become a farm. The mill machinery was stripped out and sold in 1929. The mill house and its farmland were sold off in 1957 and much of the land was built on … and the mill itself became abandoned and derelict. It was restored and converted into a private house in 1986-88, with some alteration to the original building and its grounds. The mill pond was filled in and is now a garden lawn. (Chatwin, p.8)
The name Sandford is, not suprisingly, an old one. It means – wait for it – a ‘sandy ford’. Saunfford was how it appeared in its first known reference in 1216, and it became established as part of a tithing name – Westall, Naunton & Sandford Tithing. The sandy ford in question is best shown on Merrett’s map below, dated 1834. It was essentially a large puddle in the middle of the Old Bath Road where the original course of the River Chelt flowed across the public highway to meet up with its diverted other half.
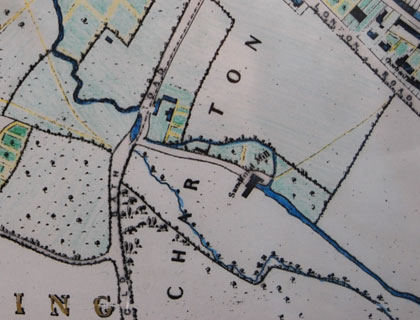
1834 map (with normal “north at the top” orientation). Sandford Mill, standing alone in the fields, was reached via an ancient lane off the Old Bath Road, shown here unnamed. It did have a name though: Mill Road, and it culminated in a small bridge over the mill leat and a footpath across the fields to London Road, coming out approximately where Chelsea Close is today. Notice that the small stream running down from London Road to the mill is not marked on this map; whether it was dried up, culverted or simply omitted I don’t know.
Mill Road doesn’t exist any more, except as fragments of private driveway. Its demise came in 1839, just a few years after this map was made, when present day Sandford Mill Road came into existence to join up London Road with the Old Bath Road, brutally slicing through the old road. The new road was constructed by Charles Cooke Higgs, of Langton House in London Road (now a pub). It seems to have existed only as a fairly primitive road for many years though, only being properly made up and adopted as a highway in the 1920s.
–

Here it is … the River Chelt flowing out from beneath Sandford Mill Road. At this point, anyone not familar with Cheltenham’s premier watercourse is probably thinking “Hnh? Is that it?” Yes, the River Chelt is small and humble and unassuming. If you were expecting something like the magnificent expanse of the River Avon in Bath, tumbling over silky weirs and gliding majestically between spans of honey-stone Georgian bridge piers and romantically traversed by boats, you’d be disappointed. The Chelt is pushing its luck even to be called a river – it’s just a little country brook whose depth and flow would not greatly trouble a pair of wellies. In fact it’s so small it has the ignominy of being named after the town, and not vice versa. In fairness to it though, it used to be bigger.
The Chelt is a “flashy” river. It appears so innocuous it’s difficult to imagine it could be capable of bursting its banks, and if it did you would imagine it could do no more than wet your ankles. But the hidden power of the Chelt is that it swells very fast. It can rise to flood levels in as little as two hours. Its danger is a happenstance of topography: rainfall on the Cotswolds drains swiftly off the slopes and into the valley where the infant river gathers pace. A few hours of exceptionally heavy rain on the hills can bloat the Chelt into a small monster. As it rushes down the steep slope towards the urban area it is joined by the Ham Brook and Lilley Brook, themselves easily swelled by excess rain, and occasionally this creates a devastating surge. Despite the volatility and risk, the River Chelt is not currently included in the Environment Agency’s flood alert system. Why? Because it floods so rapidly there is no meaningful way to give advance warning. By the time a flood alert can be issued, it’s probably too late.
Originally the Chelt was faster and deeper and during the 19th century it was very prone to flood, particularly as the town got more built up and the river was diverted from its natural bed in crucial places around the town centre. Whenever flooding does occur, the diverted river seeks its original bed – not much fun for those whose houses sit in the old river course. Flooding became an increasingly serious and regular occurrence, reaching a particularly catastrophic head on 26th July 1855 when a major flooding incident brought havoc to the town centre and all but destroyed Jessop’s Nursery Gardens, a 20 acre pleasure garden on the St James’s Square site, which ended up under seven feet of water and trashed by the weight of debris swept in from other destroyed property upstream. Action was taken in the 1870s to curtail the Chelt’s destructive force by reducing its size and flow, principally by adapting its flow through the three main mills. The construction of Dowdeswell Reservoir in the hills east of the town in the 1880s enabled the Chelt’s flow off the hills to be managed, though it’s too far upstream to make a huge difference. Used for over a century as the town’s water supply, Dowdeswell Water is now a part of its flood defence, although its capacity to prevent floods is fairly limited because much of the flood surge comes from the Lilley and Ham brooks further downstream.
Both the 1806 and 1834 maps show the River Chelt’s original meandering course through the meadow south of the mill. It no longer flows this way, now restricted to its single diverted course through the mill. But the meadow still survives, despite the development of the rest of the area, as a public open space known locally as Cox’s Meadow.

Cox’s Meadow, a public park enclosed by railings, where the remains of trees along the Old Bath Road mould themselves to the ironwork like melted plastic.
A controversial Flood Alleviation Scheme was implemented in the early years of the millennium which did a great deal of damage to Cox’s Meadow: the construction of an overflow reservoir, or balancing pond, to contain any flood spillage from the river before it reaches the town. It’s an obvious choice; since Cox’s Meadow held the natural course of the Chelt before it was diverted as a mill leat, that will be the immediate place the waters will gravitate to. But the destruction of a beautiful and much loved public open space was very upsetting for residents. As it turned out, the reservoir failed to prevent the devastating flooding of the town centre in 2007, when around six hundred buildings were inundated in two close but separate incidents. The Environment Agency claim is that the flood defences were never designed to eliminate floods altogether, but rather to reduce their likelihood, that the conditions of 2007 were extreme and unstoppable and would have been much worse if the defences hadn’t been in place. The alleviation scheme is designed to protect against a 1 in 100 year flood, whereas the second of the two 2007 incidents was somewhere between a 1 in 120 and a 1 in 330 year event – far more severe than the defences could be expected to cope with. On the other hand, there are local suspicions that mismanagement of the outflow from Cox’s Meadow was to blame for at least one of the floods. Certainly there was a structural failure in the Cox’s Meadow reservoir during the first flood incident when the cross-beam above the outflow culvert collapsed under the weight of the water.
The name Cox’s Meadow can be traced back to around 1911 when Sandford Mill hung up its millstones and became a farm. The farmer at that time was a chap called William Cox. The land remained in the Cox family until 1957 when farming gave way to housing development, but the name has stuck … not only in local parlance but more formally as the name of a small roundabout on the Old Bath Road.

–
And so we come to the point where the River Chelt flows under the Old Bath Road. This is the site of what was once an important bridge known as Sandford Bridge, a significant landmark and crossing point in past centuries. Unfortunately all traces of earlier bridges are now lost and what we have now is a particularly unattractive concrete jobbie with galvanised rails and wire mesh, ugly and functional, built as part of the Environment Agency’s flood alleviation scheme. The ford was also at this spot, flowing over the road just to the right of the bridge. Although long gone, it has been known to re-establish itself temporarily in times of heavy rainfall.

The Old Bath Road is exactly what it says on the tin. It was once the main road to Bath and Cirencester, until the early years of the 19th century when the New Bath Road was constructed parallel to it. That’s a place we will reach further along the walk. This older road has existed since time immemorial, and there is a reference to the poor condition of it in 1629 in the Manor Court Books: “alta via ducens versus Sandsford Bridge … in magna ruina”. References to a road called Edge Way as far back as the 13th century very likely also refer to the Old Bath Road. A little further along where the road joins London Road was once a tree known as Gallows Oak, which was part of the town’s early criminal justice system. The tree is shown on the 1806 map above, though it had probably gone by the time genteel society descended on Cheltenham in the Regency period.
–

And now, for the first time on this walk, we have the luxury of being able to walk alongside the River Chelt instead of glimpsing it under bridges and through gardens. This is the pleasantly shady scene you get strolling down the narrow footpath which leads off the Old Bath Road just next to the bridge, which runs parallel with College Baths Road. Doesn’t it look rural and idyllic? The trees along both banks dapple the sunlight on the gently eddying stream. It’s easy to imagine that the scene here hasn’t changed in centuries, as the river looks comfortably unspoiled between its natural mud banks. However, it appears to have been drastically re-channelled during the mid 19th century. I only noticed this when I was preparing the maps for this article. Look at the straight, tidy line of the river on the 1883 map below – then scroll back up to the 1834 map, and compare the mad meanders.
College Baths Road is another street whose name reflects its function, being the site of the swimming pool belonging to Cheltenham College. The College was founded around 1860, and its baths were built a few years later, mapped here in 1883.
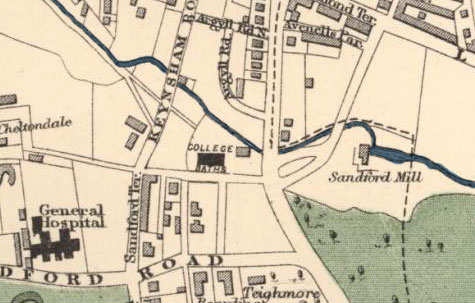
1883 map. College Baths Road is shown unnamed, but the College Baths themselves are clearly marked.
According to Sampson & Blake’s A Cheltenham Companion, the College Baths were opened c.1880, a large chunky building of pale yellow brick and believed to be the earliest surviving swimming bath in England to retain its original fixtures and fittings – it’s now a Grade II listed building. It was designed by W.H. Knight, a well respected architect of the day, and includes a poolkeeper’s cottage, seen here (late 2009) undergoing some rather drastic remodelling.

Demolition of part of the poolkeeper’s cottage. The main bath building, of similar style, is out of view. The brick tower thing in the background is part the fire station – not one of the finer moments in Cheltenham’s architectural history and earmarked for imminent replacement, though if recent planning wheezes in Cheltenham are anything to go by, I don’t hold out much hope of the new building being a visual improvement.
The shady footpath opens out onto Keynsham Road; long, straight, genteel, leafy and relatively quiet. Much of the development in this street belongs to the early 20th century, though it has a terrace of much older cottages at its southern end, which used to be known by a separate name – Sandford Terrace (see the 1883 map above). The Chelt flows underneath Keynsham Road and into the upper section of Sandford Park, a public open space which has survived here for many centuries, and the footpath continues alongside it all the way.
Keynsham Road is also where you will find Sandford Lido, an open air swimming pool considered to be among the nation’s finest. It was built in 1935 and is a beautifully preserved period piece from this era. Before the lido was built its site was occupied by the Cheltenham Corporation Water Works Pumping Station. The pumping station stood on what is now the lido’s car park, and although it’s long gone I remember there being a derelict Victorian cottage still surviving on the site in the early 1990s. A ‘Water Works Cottage’ is listed in the 1891 census, so that was probably it. In latter years the cottage sat on its own in the car park fronting directly onto Keynsham Road and looking strangely lonely and detached from its surroundings. One day around 1995 I walked past and it was gone, with only a little square patch of slightly different coloured tarmac in the car park showing where it had stood. It’s now difficult to imagine it was ever there.
One Victorian cottage which mercifully is very much still there is Glendouran Cottage.

Glendouran Cottage sits beside the new bridge in Keynsham Road with the River Chelt gliding by. My guess is that the cottage dates from around the 1880s – it’s not on the 1883 map above but doesn’t look a lot later than that. Its garden is exquisitely pretty in the summer months. And this is where I can’t help but have a little rantette. There is little dispute now that Cheltenham needed its flood defences bolstered, but this is one place where the character has been comprehensively ruined by the Flood Alleviation Scheme. When I lived in this area, this part of Keynsham Road was my favourite local spot, where the Chelt came rippling out from underneath a beautiful 19th century arched bridge made from local brick, its banks lush with water weeds. As part of the flood scheme, it was deemed necessary to flatten and mow the bank on one side to encourage floodwater to spill over into Sandford Park. Lamentably, the antique bridge was not deemed wide enough to accommodate flood flow, so it was demolished and replaced with a slabby splat of concrete topped with cheap and nasty galvanised bars. This is the classic conflict between preserving the town’s heritage and considering the needs of those who have to live with it. If the widening of the river channel saves your property from flooding then you probably look upon the loss of the historic bridge as a necessary evil. However it’s difficult to imagine how the Environment Agency could possibly have picked a more brutal, insensitive eyesore of a concrete runt. From their point of view, their job is to protect Cheltenham from floods not to preserve its historic character, and no doubt replacing the bridge with something in keeping with the style of the old one would have been too expensive. All the same – what a vile balls-up they have made of this beautiful spot.
I assume Glendouran Cottage was once part of the property of Glendouran House, which formerly stood in capacious wooded grounds on the west side of Keynsham Road, approximately where the lower end of Keynshambury Road now stands, the home of Irish alderman and philanthropist Charles Wilson and the largest of several big villas in the area.

1921 map. Glendouran House occupies a large area north-east of the Chelt, which has since been swallowed up by development in Keynshambury Road (the cul-de-sac at the top) and Keynsham Road itself. Only the cottage, located on the river bank by the ‘O’ in ‘Road’, still survives. The map shows Sandford Park shortly before it became a public park, marked here as allotment gardens, with the pumping station on land now occupied by Sandford Lido. Note also a large building on the south bank of the Chelt within the park itself and next to the footpath – there is no surviving trace of this now and I’ve no idea what it was.
Keynsham Road itself dates from around 1870, although it was a formalisation of a much older footpath of the same name. The name Keynsham can be found in a number of street names and house names in this area and the obvious conclusion is that it’s named after the town of Keynsham near Bristol. There is a connection with this – Rodney Road in the town centre is named after the Rodney family of Keynsham, connected by marriage to the solicitor Robert Hughes who built Rodney Lodge in 1806. But the name here is of much earlier origin. The fields between London Road and the River Chelt were known in the 16th century as Kyngisham, with the variants Kingsham and Kinsham emerging in subsequent centuries. The spelling may have changed a little but the pronunciation probably hasn’t.
And so as we continue to follow the River Chelt through Sandford Park on its course towards town, the first thing we are confronted with is a curious stone ornament – a rounded canopy on smooth pillars. It is in fact a non-functioning Gothic Revival drinking fountain, gifted by the Misses Whish. And here we have a point of connection with another Cheltonia article, because this fancy item of gratuitous street furniture was originally sited at Westal Green.

The Whish sisters’ drinking fountain in Sandford Park.
If you own a copy of Steven Blake’s Cheltenham: A Pictorial History, have a look at section 172 for a priceless picture of this fountain standing next to a First World War tank on Westal Green roundabout. The fountain was commissioned in 1891 by Mary, Anne and Ellen Whish as a gift to the people of Cheltenham. These three benevolent elderly sisters lived in Lansdown Parade, a few yards from Westal Green and a popular address for well-to-do maiden ladies at that time. The gift commemorated their fifty years’ residence in the town but was one of many generous deeds by these charitably minded sisters. It was joined by its unlikely martial companion in 1919; fountain and tank sat side by side for several years until it was decided to build a colonnaded neo-classical electricity substation on Westal Green roundabout in 1929 (which is still there). The tank was decanted to Montpellier Gardens, while the drinking fountain ended up here in Sandford Park, where it makes a very pleasant decorative feature, if a somewhat redundant one. Comparison with the photo in Blake’s book shows that it is missing its drinking basin, and that it also originally had some kind of pole sticking out of the top.
If you look carefully at the picture above you might notice that the ground slopes gently downwards from the right (where the River Chelt is behind the railings) towards the hedge on the left. This hedge represents the original course of the Chelt (also discernible in the field boundary shown running through the middle of the park on the 1921 map). This diversion is not recent; it goes back to medieval times when the Chelt was a vital resource for milling. It was common practice back then to divert a river slightly uphill and in a straighter course to give the mill stream more whoomph. Consequently Sandford Park is a floodplain – it has to be, because the moment the Chelt overtops its bank the water goes rushing towards its original bed, however many centuries have passed since it last lay there.
Needless to say Sandford Park forms a particularly important part of the town’s Flood Alleviation Scheme. As it is one of the few areas of the town centre which has not been built over, the flood waters are actively encouraged to spill into it and submerge the whole park, which doesn’t do a lot for the beds of colour co-ordinated pansies kindly provided by the Borough Council but is greatly preferable to the destruction of roads and properties elsewhere. To aid its usefulness as a flood defence, this portion of Sandford Park now sports a drainage outlet known locally as The Plughole. It’s a vertical shaft in the heart of the floodplain which funnels the water down into a hidden culvert which runs underneath College Road and comes out some way downstream at the other end of the park.
Another feature of the upper section of Sandford Park is easily overlooked on account of being a mess of ivy and graffiti, but is in fact a remnant of a significant place in Cheltenham’s history. For this single-storey whitewashed hulk of a broken down building next to the Chelt at the side of College Road is the last surviving building of the Chalybeate Spa which, in 1801, was the first new spa to open at the start of the Regency spa boom.

It was founded by William Humphris Barrett, a well-known Cheltenham character during that period and the person after whom Barrett’s Mill is named. Barrett owned much of the land now occupied by Sandford Park, and in his day it was part of the property of the mill – and all within the same field, because College Road which now slices Sandford Park in half did not exist in those days. Since time immemorial, local people had been visiting a spring on the river bank whose water emerged “in a very sparing quantity, depositing in its course a yellow ochery matter”, according to Griffith’s Cheltenham Guide of 1818, and “drank it successfully as a lotion in weaknesses, and other complaints of the eyes.” The iron-rich water was a diuretic and commended by doctors for nervous diseases, convulsions, chronic inflammation of the eyes and ‘sterility in females’. Around 1801 it was discovered that this sparse and precious medicinal spring was merely an offshoot of a much more copious spring further down the meadow, and Barrett, being a canny sod, built a spa house over this and charged people for access to it. He also built a residential villa beside it and laid out “gravelled walks to the upper part of the town, from which it is distant but a few hundred yards.” These paths were along the south side of the Chelt where the footpath through Sandford Park still runs today.
At that time there was no direct access from the High Street, and so visitors to the spa had no choice but to walk to it along the footpaths from Barrett’s Mill. The town’s Paving Commissioners were keen to open up the High Street to make a new access to this popular spa, but Barrett wasn’t having any of it and it was recorded at a meeting in September 1827 that he refused “on any terms” to allow the new road on his land.
–

1806 map of the Chalybeate Spa and Mill (south-west is at the top). The mill is now known as Barrett’s Mill, but named here as Cheltenham Mill. The main road is the High Street, then only sparsely built up along this particular stretch. Certain familiar streets such as College Road and the top and bottom ends of Bath Road didn’t exist at this time. However there are some you may recognise: Barratt’s Mill Lane, Vernon Place, Bath Street and Cambray Place are all shown here, while the house marked as the property of Sir William Hicks Beach is what later became the Belle Vue Hotel, still surviving as residential flats. The meandering Chelt is shown in its old course through the town, soon to be diverted and culverted as the Regency building boom took place.
The surviving chunk of the spa is the residential house, variously known as Chalybeate Spring Villa and Field Lodge. It was a beautiful Regency villa with a decorative tented canopy over the front door and a fine walled garden. Its degeneration into the vandalised shell you see today most likely came about in 1927 when Sandford Park was founded. The council used a compulsory purchase order to turf out the James family who had lived in the house for forty years, and their home became a tool shed, its upper storey demolished and its windows bricked up. The building which housed the spa itself has fared even less well … it has been replaced by the parks department offices.
College Road was laid down in 1842, after Barrett had passed on and the Sandford Park land was owned by Sir Matthew Wood, a local solicitor. His plan was to build handsome villas all the way along it on both sides, and also to carve out a new and highly ambitious crescent development from the Bath Road, starting roughly on the present site of Bath Road car park and sweeping across what is now the St Luke’s area. However Sir Matthew died before his plans had got very far, and most of his ideas died with him. College Road was initially known as Sir Matthew Wood’s Road, or simply Wood’s Road. It comes out beside the College grounds, but when you bear in mind that the College wasn’t there until the early 1860s, it’s obvious that College Road can’t have been its original name. It passes right by the chalybeate spa but was no longer necessary as an access route to it, as spas were in decline by then, and was simply put through as a link from the High Street to Sandford Road. Construction of the road necessitated the demolition of several cottages in the High Street, including one called Chalybeate Cottage which may have once been part of the spa property. Initially the road didn’t line up with Hewlett Road as it does today; this was achieved by widening and realignment of the junction in 1871.
–

The Chelt flows under College Road just behind the remains of the Chalybeate Spa. Mercifully this Victorian bridge was spared the ravages of the Flood Alleviation Scheme, probably because it has a bypass culvert next to it which takes any overflow water away from the bridge through a pipe under the park. The culvert is not new, but its inlet was formerly covered. The flood scheme involved opening it up to make it more free flowing, hence the large metal safety screen you can see on the left of the picture.
And so – if you cross over College Road at the conveniently positioned pedestrian traffic lights and continue to follow the river, you find yourself in the lower section of Sandford Park, where the footpath continues along the bank in exactly the same way as before. You can pause here and imagine what it would have been like in earlier centuries before College Road was built, when the path continued without interruption.
The view on the other side of the river is mostly of the walls and back gardens of houses which line the adjacent street, which in this case is the High Street. The Chelt runs in a parallel course to the High Street, reflecting the fact that both street and river were the original heart and focus of Cheltenham. Some of the walls are very old and some are integrated with both older and newer bits. You can also see some of the buildings between the trees.
–

The backs of houses which front onto the High Street, viewed from the bank of the Chelt in Sandford Park.
–
At the town end, the park is heavily landscaped with rockeries and rivulets laid out for the inauguration of Sandford Park in 1927. The ornamental mini-streams, slow flowing and pond-weeded, were there long before 1927 however. You might recognise them on this map made a century earlier, when they were part of the mill complex.

1820 map (south at the top) showing Cheltenham Mill (Barrett’s Mill) in the upper section of Sandford Park, which was apparently wooded at that time, with the edge of the Chalybeate Spa building on the left. The wobbly field margin at the top of the map here shows the original course of the Chelt before its medieval re-routing.
As in the upper section, the bulk of lower Sandford Park is a flood plain, and the original course of the Chelt was along the lowest lying land, which is roughly where the bottom of St Luke’s Place is today. The river which we are following here is not the natural one but a medieval mill stream. At the top end of the park it passes over a series of small weirs on its way to the sluice which once powered Barrett’s Mill.
–

Mini weirs in the run-up to Barrett’s Mill.
In the grand scheme of Cheltenham’s origins and history, Barrett’s Mill is a fundamental hub. There has been a mill on this site for so many centuries its origins are not recorded. It was listed in Domesday in 1086. At one time known as Cambray Mill, it was marked as Cheltenham Mill on the early 19th century maps, reflecting its importance over the other mills in the town. The present building doesn’t look very special at first glance; I am guessing that it dates from the early or mid 19th century, but it was ‘modernised’ around the 1980s which seems to have involved decking it out with inappropriately trendy windows and rendering the outside with some thick whirly Artex stuff which would look more fitting as cake icing than the surface of a historic building. The front of the mill rises straight out of the mill pond … and the Chelt rushes through a narrow sluice down one side of it, so it is half surrounded by water.

Barrett’s Mill undergoing structural renovations in late 2009. The building on the left, sensitively designed, is modern.
–

In front of the building is the millpond, looking very much as it would have done in past centuries … a wide pool of a deep glassy green with the rich scent of rushing water. It hasn’t always been this pleasant though. In 1853 the Central Board of Health sent a surveyor to Cheltenham from London to assess the need for improved sewerage, who reported that the River Chelt “is in an exceedingly bad state, and has long been a fruitful source of disease and injury. Along its course are three water mills, the dams of which, penning back the foul matters discharged, constitute so many huge open cesspools which in warm weather are intolerable and from which in times of flood the water and filth flow back into the houses, an evil which has occurred three times in six weeks.” (Hart, p.340)
–

The channel out from the millpond is formed by an old curved wall, where Regency brick is founded on slabs of Cotswold stone.
It’s hard to imagine this now, but the millpond at Barrett’s Mill once had a channel running through to the High Street. A board was fixed across the sluice with three holes drilled through it of very particular sizes, and the River Chelt was required to run permanently through these holes, which controlled its flow, and down the High Street. The street was traversable only by stepping stones and planks, and residents used the stream for their ablutions and laundry requirements, at least on those occasions when it was clean enough. The street was prone to clog up with mud, and the plank bridges used to sink down and get stuck in it, so the sluice gate had to be periodically opened by the miller, which sent the main torrent of the Chelt gushing down the High Street. This was required to be done once, twice or three times a week at different times in history.
Evidently this arrangement caused a significant conflict of interest between the miller and the rest of the inhabitants. That successive generations of millers failed repeatedly in their obligations, even under threat of injunctions, fines and big beefy bailiffs, is evidenced in the Manor Court Rolls over several centuries. A court order of 1561 demands the installation of a sluice “in the place accustomed” along with a board with three holes: “One hole to be bored with a yoke and the second with an inch auger, and the third with a three-quarter inch auger”. Six years later the same miller was in trouble again for not keeping the water levels in the millpond high enough to flow through the holes, and was subjected to weekly inspections and the threat of a large fine (Hart, p.64). These orders come up frequently through the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries, until the idea of slopping water down the High Street was abandoned in about 1786, when the gentrification of the town required a decent road to be made there with the water confined to small channels either side of it. An attempt was made to resume the full flush in the early 19th century during the tenure of William Humphris Barrett, who with characteristic recalcitrance flatly dug his heels in and failed to comply with a slew of demands, threats and court orders which were piled onto him from at least 1807 to 1822, until the town got its own water company and alternative arrangements were made for cleaning the streets. At some point the Chelt was diverted away and it’s not now possible to work out where the original sluice was or what course the river took towards the High Street.
–

As the Chelt trickles away from the millpond and towards the town centre it retains something of a rural idyll – hard to imagine this stretch of water is just yards from the busy Bath Road.
During Barrett’s time, the mill underwent considerable expansion. By 1834 there was a large complex of outbuildings on the site, including a truly enormous chimney which stood to the south of the mill at the top of the slope where the rockeries are now. The chimney survived even after all the other outbuildings had disappeared and was demolished in 1907. Amina Chatwin’s fascinating article Cheltenham Mills (see below) includes an extraordinary photo of it from the Cheltenham Chronicle and Graphic of 1907.
William Humphris Barrett has the distinction of being forever associated with the mill and its surrounding area. While other millers came and went for the best part of a millenium on this site, Barrett’s strength of character made him memorable, and the mill has gone down in history not as Cheltenham Mill or Cambray Mill but as Barrett’s Mill. Even the tiny medieval lane running down to the mill from the High Street is named after him. Unfortunately for him though, it is misspelt.

–
Here’s a map of the area just before Sandford Park was founded. The layout has not changed significantly since then, except that the buildings shown here to the left of the lower weir are all gone and the site is now Bath Road car park. This point is significant as the first place, albeit brief, where the River Chelt disappears into a culvert.

1921 map
And so begins the stage of our walk where the Chelt becomes invisible. It disappears into its first culvert in the corner of Bath Road car park. You can go and peer over the wall and see the junction, newly made with charming fresh concrete as part of the Flood Alleviation Scheme. From here the river trundles along under the car park and comes out on the other side of Bath Road … but once again this is a historical diversion. You may notice on the map above that the section between Bath Road and Wellington Street is rather straight and simple, a hint of an artificial course. The actual course of the Chelt here was once loopy and meandering, and the loops were underneath these buildings …

1820s houses in the Bath Road. These are shown on the 1921 map just to the south of the Chelt. Originally they would have been slap bang on top of it – though it may have been diverted just before they were built.
–

Now the Chelt doesn’t go under the buildings, it takes this straight course through to Wellington Street. The reason for the diversion is nothing to do with the mill this time – it dates back to the long vanished Wellington Mansion and its one time owner, Colonel Riddell, who wanted the River Chelt to run through the middle of his garden – so he had it moved.
Notice the relics of early street furniture here. A set of municipal railings has been provided to deter hapless pedestrians from flinging themselves in the River Chelt as it emerges from its culvert, and these are set into a stone pier which is perhaps now the only surviving remnant of Wellington Mansion, once forming part of its boundary along the Bath Road, when it would have been much more green and open. To the left of the pier in the above photo and backed with some charming corrugated iron are a few – a very few – early railings. I’m not sure whether these belonged to Wellington Mansion or the row of 1820s houses on the left, but they look like they are contemporary with the stone pier and they are topped with some rather unusual and distinctive finials … a very flat and stylised Greek anthemion design. Other better preserved examples of these finials can be found elsewhere in the town centre (e.g. Regent Street).
–

Detail of the stone pier (and one of the anthemion railings)
This concludes part one of our River Chelt walk, and yet the story is only just getting started. Part two will explore the course of the river, seen and unseen, through the middle of town. It will start right here, in the picture below, where the Chelt flows through what was once the garden of Wellington Mansion and into Wellington Street.

–
Bibliography for this article:
Cheltenham Mills by Amina Chatwin, from the journal of the Gloucestershire Society for Industrial Archaeology (available online)
River Chelt Flood Event Performance Review (September 2007), report compiled by Halcrow Group Limited on behalf of the Environment Agency, pdf available on the Environment Agency’s website
A History of Cheltenham by Gwen Hart (1965)
and as always, the Historical Gazetteer of Cheltenham compiled by James Hodsdon








